Details
Ensuring Precision: The Importance of Calibration and Calibration Services in Modern Industry
Introduction
In today's technologically advanced and highly competitive industrial landscape, maintaining precision and accuracy in measurements is paramount. Calibration, the process of configuring an instrument to provide a result for a sample within an acceptable range, plays a crucial role in ensuring that measurements are reliable and accurate. Industries ranging from aerospace and healthcare to manufacturing and telecommunications rely heavily on precise measurements to guarantee quality, safety, and efficiency.
(1).png)
Calibrated Connection
Calibration services, provided by specialized professionals, are essential for achieving and maintaining this level of accuracy. These services involve the verification and adjustment of measurement instruments to align with established standards, ensuring that they deliver accurate and consistent results. The significance of calibration and calibration services cannot be overstated, as they are fundamental to meeting regulatory requirements, enhancing product quality, and optimizing operational performance. Adherence to international standards such as ISO 17025 further validates the credibility and reliability of calibration processes, ensuring that measurement results are traceable and recognized globally.
In this article, we will delve into the critical aspects of calibration and the indispensable role of calibration services in modern industry. We will explore the different types of calibration, the benefits of utilizing professional calibration services, and the future trends shaping this vital field. By understanding the importance of these practices, businesses can make informed decisions to uphold the highest standards of precision and reliability in their operations.
In this article, we will delve into the critical aspects of calibration and the indispensable role of calibration services in modern industry. We will explore the different types of calibration, the benefits of utilizing professional calibration services, and the future trends shaping this vital field. By understanding the importance of these practices, businesses can make informed decisions to uphold the highest standards of precision and reliability in their operations.
How often should my instrument be calibrated?
The question isn't whether to calibrate, it's how often to! The frequency of calibration depends on:
- Manufacturer-recommended calibration interval. Manufacturers' specifications indicate how often to calibrate their instruments,
- How important the measurements being made are to your product or service;
- The degree of wear and tear that the instrument will experience in service;
- The stability of the instrument itself and a review of the calibration records that already exist to determine whether adjustment has been needed previously.
General recommendation is a starting periodicity of 12 months for most instruments and may increase the calibration frequency to half-yearly or quarterly if adjustment is required or reduce to 2 years if equipment is fairly stable after a sequence of annual calibrations.
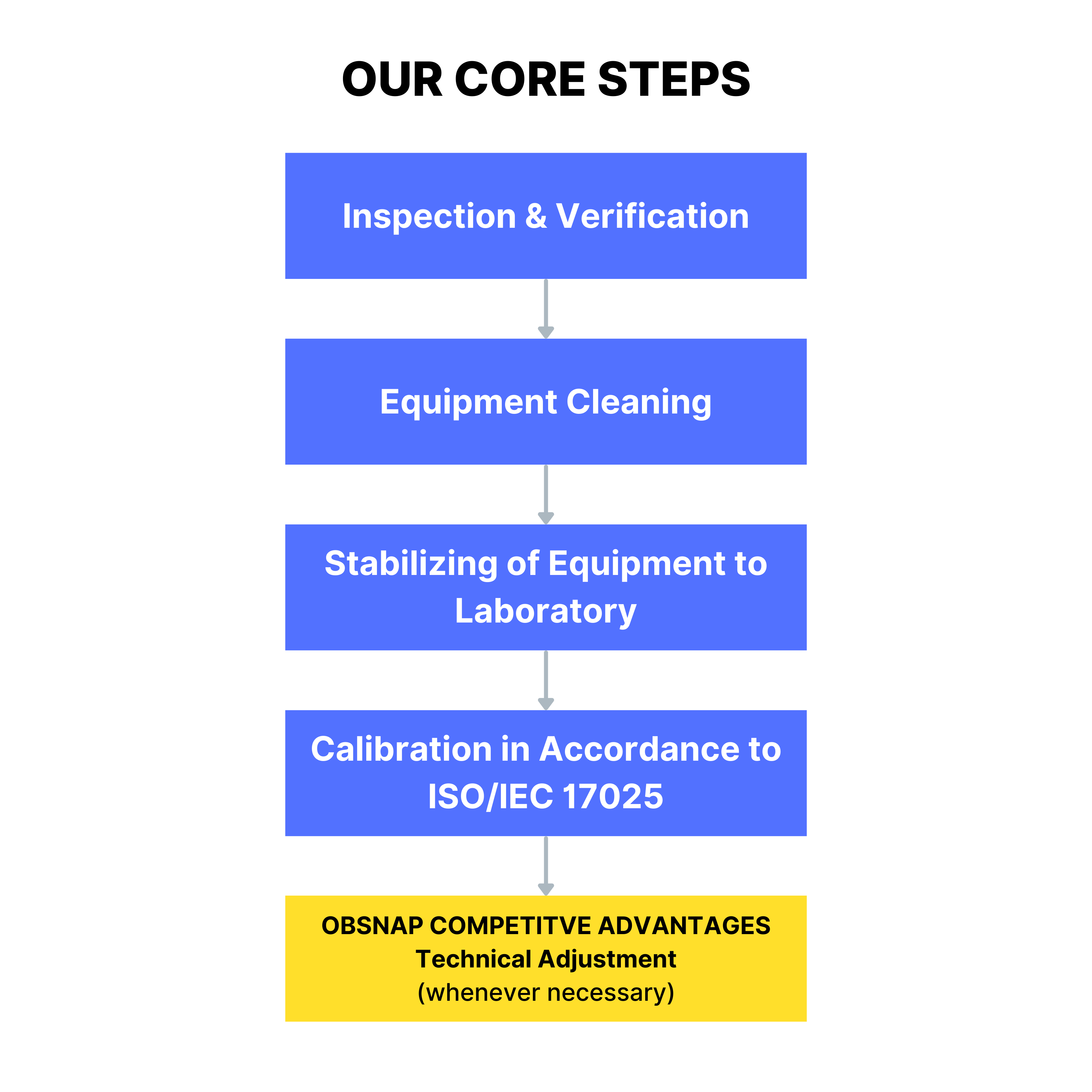
Section 1 : Understanding Calibration and Calibration Services
What is Calibration?
Calibration is the process of configuring an instrument or device to provide measurements within an acceptable range by comparing it with a known standard. This process ensures that the instrument's readings are accurate and reliable, which is crucial for maintaining quality control, ensuring safety, and complying with regulatory standards. Calibration involves adjusting the instrument to eliminate or minimize errors, thus ensuring that its output aligns with the true value. Adherence to internationally recognized standards such as ISO 17025 further validates the credibility and reliability of calibration processes, ensuring that measurement results are traceable and recognized globally.
The need for calibration arises because measurement instruments can drift over time due to factors such as wear and tear, environmental conditions, and usage. Regular calibration helps detect these deviations early, allowing for timely corrections and maintaining the integrity of measurement data.
Types of Calibration
Calibration can be classified into several types based on the nature of the instruments and the parameters being measured. The main types include:
- Electrical Calibration:
- Purpose: Ensures the accuracy of electrical measurement devices such as multimeters, oscilloscopes, and power supplies.
- Instruments: Voltage, current, resistance, and frequency measuring instruments.
- Procedure: Comparing the instrument's readings against a known standard and adjusting accordingly.
- Mechanical Calibration:
- Purpose: Validates the accuracy of mechanical instruments used in measuring physical dimensions and forces.
- Instruments: Calipers, micrometers, torque wrenches, and pressure gauges.
- Procedure: Comparing measurements with standardized gauges or weights and adjusting the device to match these standards.
- Thermal Calibration:
- Purpose: Ensures that temperature-measuring devices provide accurate readings.
- Instruments: Thermometers, thermal cameras, and temperature controllers.
- Procedure: Comparing the instrument's readings with a known temperature standard, such as a calibrated temperature bath or a reference thermometer.
- Dimensional Calibration:
- Purpose: Ensures the accuracy of devices that measure physical dimensions.
- Instruments: Rulers, gauges, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM).
- Procedure: Comparing the instrument's measurements against reference standards like gauge blocks or calibrated dimensions.
- Mass Calibration:
- Purpose: Validates the accuracy of instruments that measure weight.
- Instruments: Balances and scales.
- Procedure: Comparing the device's measurements with standardized weights and making adjustments as needed.
+ Section 2 : The Role of Calibration in Industry
Calibration is a critical process in various industries, ensuring that instruments and equipment perform accurately and consistently within specified limits. It involves comparing the measurements of an instrument or device to a known standard, making necessary adjustments to align with the standard.
Accuracy and Precision
Accuracy and Precision
- Accuracy:
- Definition: Accuracy refers to how close a measurement is to the true or accepted value.
- Importance in Industry: Accurate measurements are vital for ensuring the quality of products and services. In industries like pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, and aerospace, high accuracy is essential for safety, efficacy, and customer satisfaction.
- Calibration's Role: Calibration ensures that instruments measure accurately by comparing them to a standard. Regular calibration helps detect and correct any deviations from the true value, thus maintaining the instrument's accuracy over time.
- Precision:
- Definition: Precision is the degree to which repeated measurements under the same conditions yield the same results.
- Importance in Industry: Precision is crucial for consistency in processes and products. In industries such as food and beverage, precision ensures that products meet quality standards batch after batch.
- Calibration's Role: While calibration primarily ensures accuracy, it also helps identify issues affecting precision, such as instrument wear or environmental factors. By maintaining both accuracy and precision, calibration supports the reliability of measurement systems.
Regulatory Compliance
- Industry Standards:
- Purpose: Regulatory bodies and industry standards organizations set guidelines for calibration to ensure safety, quality, and efficiency.
- Examples: Organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provide standards for calibration procedures, including ISO 17025.
- Compliance Requirements: Many industries are required to adhere to these standards to operate legally and maintain certifications. For example, ISO 9001 certification requires regular calibration of measurement equipment.
- Quality Management Systems (QMS):
- Integration: Calibration is a critical component of Quality Management Systems in many industries. A well-maintained QMS ensures that all instruments are calibrated and records are kept, demonstrating compliance during audits.
- Documentation: Detailed records of calibration activities are necessary for compliance. These records help trace the history of an instrument’s accuracy and reliability, providing evidence during regulatory inspections.
- Risk Management:
- Minimizing Risks: Regular calibration helps identify and mitigate risks associated with inaccurate measurements, such as product recalls, safety hazards, and legal liabilities.
- Regulatory Audits: Regulatory bodies may conduct audits to verify compliance with calibration standards. Non-compliance can result in fines, sanctions, or suspension of operations.
+ Section 3 : Calibration Services: An Overview
Calibration is a critical process in various industries, ensuring that instruments and equipment perform accurately and consistently within specified limits. It involves comparing the measurements of an instrument or device to a known standard, making necessary adjustments to align with the standard. Adherence to ISO 17025 is crucial in this context, as it provides a framework for ensuring the competence of calibration laboratories.
What Are Calibration Services?
.png)
What Are Calibration Services?
- Definition:
- Calibration services involve the process of verifying and adjusting the accuracy of measuring instruments by comparing them to known standards. This process ensures that the instruments produce measurements that are within acceptable limits.
- Components of Calibration Services:
- Verification: Checking the instrument against a standard to determine its accuracy.
- Adjustment: Making necessary adjustments to bring the instrument within specified limits.
- Documentation: Providing detailed reports and certificates of calibration that document the instrument's performance and any adjustments made.
- Traceability: Ensuring that the calibration process is traceable to national or international standards, often through a chain of comparisons leading back to a recognized standard.
- Types of Instruments Calibrated:
- Calibration services can be applied to a wide range of instruments, including:
- Electrical: Multimeters, oscilloscopes, signal generators.
- Mechanical: Pressure gauges, torque wrenches, micrometers.
- Thermal: Thermometers, temperature sensors, thermal cameras.
- Analytical: Spectrometers, chromatographs, balances.
- Calibration services can be applied to a wide range of instruments, including:
- Calibration Laboratories:
- Calibration services are often provided by specialized laboratories equipped with precise reference standards and controlled environments to ensure accurate calibration. These laboratories are typically accredited by relevant authorities to perform calibrations, adhering to standards such as ISO 17025.
.png)
Benefits of Professional Calibration Services
- Ensured Accuracy and Reliability:
- High Precision: Professional calibration services use highly accurate reference standards and sophisticated techniques to ensure the highest level of precision.
- Consistency: Regular calibration maintains the consistency of measurements over time, which is critical for processes that rely on precise data.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Meeting Standards: Professional calibration services ensure that instruments comply with industry standards and regulatory requirements, which is crucial for legal operation and maintaining certifications.
- Audit Readiness: Proper calibration and documentation help organizations prepare for and pass regulatory audits with ease.
- Extended Equipment Life:
- Maintenance: Regular calibration can identify wear and tear or potential issues with instruments before they lead to failures, thereby extending the life of the equipment.
- Optimal Performance: Well-maintained instruments perform optimally, reducing the risk of costly downtime or malfunction.
- Cost Savings:
- Minimized Errors: Accurate instruments reduce measurement errors, which can lead to significant cost savings by avoiding product recalls, rework, and waste.
- Improved Efficiency: Reliable measurements enhance process efficiency and productivity, resulting in better resource utilization.
- Enhanced Quality and Safety:
- Product Quality: Accurate measurements are essential for maintaining high product quality, which can improve customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
- Safety: In industries like healthcare, aerospace, and food production, precise measurements are crucial for safety. Calibration services ensure that instruments used in these fields provide accurate readings, thereby protecting consumers and employees.
- Traceability and Documentation:
- Calibration Certificates: Professional calibration services provide detailed calibration certificates that include the results, uncertainties, and traceability information, complying with standards such as ISO 17025.
- Historical Records: Maintaining a history of calibration records helps in tracking the performance and trends of instruments, aiding in predictive maintenance and quality control.
+ Section 4 : Choosing a Calibration Service Provider
Selecting the right calibration service provider is crucial for ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and compliance of measurement instruments in your organization. Consideration of various criteria and asking pertinent questions can help you make an informed decision.
Criteria for Selection
(1).png)
Criteria for Selection
- Accreditation and Certification:
- Look for providers accredited by recognized bodies such as ISO/IEC 17025, which ensures competency in calibration procedures.
- Check if the provider holds relevant certifications for specific industries (e.g., FDA for pharmaceuticals, NIST for laboratories).
- Technical Expertise:
- Assess the provider's technical capabilities and expertise in calibrating the types of instruments relevant to your industry.
- Inquire about the qualifications and experience of their calibration technicians.
- Traceability and Standards Compliance:
- Ensure that the provider follows traceable calibration procedures aligned with national or international standards, including ISO 17025.
- Verify if they use calibrated reference standards with known uncertainties.
- Turnaround Time and Service Level Agreements (SLAs):
- Evaluate the provider's turnaround time for calibration services and whether they offer expedited options if needed.
- Discuss SLAs to ensure timely calibration and minimize downtime of critical instruments.
- Range of Services:
- Consider whether the provider offers calibration services for the full range of instruments and equipment used in your organization.
- Check if they provide on-site calibration services for instruments that cannot be easily transported.
- Quality Management Systems (QMS):
- Inquire about the provider's QMS and their commitment to quality assurance, documentation, and continuous improvement.
- Ask for examples of their calibration certificates and reports to assess their thoroughness and clarity.
- Customer Support and Communication:
- Assess the provider's responsiveness and accessibility for inquiries, scheduling, and support.
- Determine if they offer technical assistance or consultation beyond calibration services.
- Cost and Value:
- Compare pricing structures and ensure transparency regarding costs for calibration services, including any additional fees.
- Consider the overall value proposition, balancing cost with the quality and reliability of services provided.
(1).png)
+ Conclusion
In summary, calibration and calibration services play a pivotal role in ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and compliance of measurement instruments across various industries. Here's a recap of the key points:
- Importance of Calibration:
- Calibration is essential for maintaining the accuracy and precision of measurement instruments, ensuring that they provide reliable data for decision-making, quality control, and regulatory compliance.
- Accurate measurements are critical for product quality, safety, and customer satisfaction in industries ranging from healthcare and aerospace to manufacturing and food production.
- Role of Calibration Services:
- Calibration services involve specialized procedures to verify and adjust instruments against known standards, ensuring their accuracy and reliability.
- Professional calibration services, particularly those adhering to ISO 17025 standards, offer benefits such as ensured accuracy and reliability, regulatory compliance, extended equipment life, cost savings, enhanced quality and safety, traceability, and documentation.
- Calibration service providers use ISO 17025 accredited laboratories, technical expertise, traceable calibration standards, and quality management systems to deliver high-quality calibration services.
View more about Calibration Services on main site

